- Exemption limit extended from 1,60,000 to 1,80,000
- No change in women tax exemption limit i.e. 1,90,000
- Senior citizen exemption 2,50,000; age now 60 years not 65
- Citizens over 80 years have exemption limit of Rs. 5 lacs
Thursday, April 21
Union Budget: 28-2-2011
Powers and Functions of State Bar Council:
Sec 6 of Advocates Act 1961 deals with the Powers and Functions of State Bar Council:
(a) to admit persons as advocates on its rolls;
(b) to prepare and maintain such rolls;
(c) to entertain and determine cases of misconduct against advocates on its roll;
(d) to safeguard therights, privileges and interests of advocates on its roll;
(e) to promote and support law reform;
(ee) to conduct seminars and organize talks on legal topics by eminentjurists and publish journals and papers of legal interest;
(eee) to organize legal aid to the poor n the prescribed manner;
(f) to manage and invest the funds of the Bar Council;
(g) to provide for the election of its members;
(h) to perform all other functions conferred on it by or under this Act;
(i) to do all other things necessary for discharging the aforesaid functions.
Judicial Activism
Judicial Activism may be taken to mean the movements of the judiciary to probe into the inner functioning of the other organs of the Government (i.e. the executive and legislature). The Judicial Activism is, no doubt, the result of inactiveness on the part of the executive and legislature.
The main object of Judicial Activism is to maintain the rule of law in the country.
The main object of Judicial Activism is to maintain the rule of law in the country.
Definition:P.I.L.
The words 'Public Interest' has been defined in Black's Law Dictionary (6th Ed.) as something in which the public, the community at large has some pecuniary interest or some interest by which their legal rights or liabilities are affected.
In Janata Dal v/s H.S.Choudhary, P.I.L. has been defined as a legal action initiated in a court of law for the enforcement of public interest or general interest in which the public or a class of the community have pecuniary interest or some interest by which their legal rights or liabilities are affected.
Wednesday, April 20
Lok Adalat
The abnormal delay in the disposal of cases in law courts is a big clot on the Indian Judicial System. The concept of the lok adalat is one of the remedies suggested in the recent years to overcome this delay but it can be effective only in those cases in which the parties are likely to arrive at a compromise.
The lok adalat will resolve disputed which have not yet gone to the court of law and disputes which are pending in the court of law. The lok adalat will resolve the disputes by way of negotiation, settlement and conciliation.
The lok adalat will resolve disputed which have not yet gone to the court of law and disputes which are pending in the court of law. The lok adalat will resolve the disputes by way of negotiation, settlement and conciliation.
Legal Aid
Its aim is to strike at the root of the problem of poverty by seeking to change the social and economic institutions and at the same time, educate and organize the poor so that they may become conscious and powerful and the institutional changes may become permanent.
Legal Literacy
The Legal Literacy may compose of the followings:
- Literacy Sivir
- Publication of legal literature and its free distribution
- Para Legal clinic
- Para Legal services
Para-legal Services:
It means rendering any legal service to the poor person of the society in connection to solve their legal problems or to safeguard their legal rights or to provide their legal rights.
It may compose of the following elements:
It may compose of the following elements:
- Para Legal Clinic
- Para Legal Training
- Legal aid services
- Literacy
The following are the ways of providing Para Legal Services:
- Provision of Legal Programme
- Provision of Legal Education
- Provision of free legal aid
- Provision of free legal assistance
- By amicable settlement
- Settlement through Lok Adalat
- To provide justice through P.I.L.
Medical aid tells what type of aid is required is surgery, medicine, E.N.T. etc. likewise para legal training tells what type of aid is required to the victim.
Scope of Public Interest Litigation
- Prisoner's rights and prison administration
- Protection of bonded, contract and child-labour
- Amplifying the scope of right to life
- Protection of environment
- Political corruption and crime
Landmark Innovations of P.I.L.
- Expanding horizons of Locus Standi rule
- Evolving epistolary jurisprudence
- Appointing socio-legal commissions of inquiry
- Monitoring laws and judicial orders
- Enforcing public duties
Latin Maxims:
Ab Initio: from the beginning
Act interim: in the meanwhile
Ad Velorem: According to value
Alibi: a plea of the accused that he was elsewhere when the offence was committed
Amicus curiae: friend of the court
caveat-emptor: Let the purchaser beware
Damnum sine injuria: damage without injury
De facto: In fact
De jure: In law
Decree nisi: A decree takes effect after specified period
Ejusdem generis: Of the same kind or nature
Fait accompli: Accomplished fact
Injuria sine damno: Injury without damage
Lis pendens: pending suit
Mens rea: A guilty mind
Obiter dicta: An opinion of law not necessary for decision
Res judicata: Case a;ready decided
Ultra vires: Risk taken voluntarily is not actionable
Act interim: in the meanwhile
Ad Velorem: According to value
Alibi: a plea of the accused that he was elsewhere when the offence was committed
Amicus curiae: friend of the court
caveat-emptor: Let the purchaser beware
Damnum sine injuria: damage without injury
De facto: In fact
De jure: In law
Decree nisi: A decree takes effect after specified period
Ejusdem generis: Of the same kind or nature
Fait accompli: Accomplished fact
Injuria sine damno: Injury without damage
Lis pendens: pending suit
Mens rea: A guilty mind
Obiter dicta: An opinion of law not necessary for decision
Res judicata: Case a;ready decided
Ultra vires: Risk taken voluntarily is not actionable
Meaning:
Accomplice: Companion in evil deeds, associate in crime
Which causes death: Fatal
A young female horse: Filly
Short story intended to give moral teaching: Fable
A person who always looks at the brighter side of things: Optimist
Simple story designed to teach moral lesson: Parable
Atheist: one who believes in the existence of God
Which causes death: Fatal
A young female horse: Filly
Short story intended to give moral teaching: Fable
A person who always looks at the brighter side of things: Optimist
Simple story designed to teach moral lesson: Parable
Atheist: one who believes in the existence of God
Defences in Criminal Contempt:
- Innocent publication and distribution of matters
- Fair and accurate report of judicial proceedings
- Fair criticism of judicial act
- Bona fide complaint against the presiding officers of the subordinate court
- No substantial interference with due course of justice
Defences in Civil Contempt:
- Disobedience or breach was bot willful
- The order has been passed without jurisdiction
- Order disobeyed is vague or ambiguous
- Order involves more than one reasonable interpretation
- Compliance with the order is impossible
- No knowledge of order
Admission and Enrolment of Advocates:
- Senior advocates and other advocates (S.16)
- Persons who may be admitted as advocate on a state roll
- Disqualification for enrolment
- Authority to whom application for enrolmnt may be made
- Disposal of applications for admission as an advocate
- Removal of names for enrolment of certain Supreme Court advocates
- Disputes regarding seniority
- Certificate of enrolment
- Right of pre-audience
Saturday, April 16
Probability
| http://www.indiabix.com/aptitude/probability/ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Reasoning

| A. |
| B. |
| ||||||
| C. |
| D. |
|
Answer: Option C
Explanation:
This is an alternating series. In the first segment, the letter "E" faces right, then down, then right. In the second segment, the letters all face down. To follow this pattern, in the fourth segment, the letters must all face up.
Maths
| Six years ago, the ratio of the ages of Kunal and Sagar was 6 : 5. Four years hence, the ratio of their ages will be 11 : 10. What is Sagar's age at present? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Answer: Option A Explanation: Let the ages of Kunal and Sagar 6 years ago be 6x and 5x years respectively.
 10(6x + 10) = 11(5x + 10) 10(6x + 10) = 11(5x + 10) 5x = 10 5x = 10 x = 2. x = 2.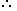 Sagar's present age = (5x + 6) = 16 years Sagar's present age = (5x + 6) = 16 years |
Maths
How many 3-digit numbers can be formed from the digits 2, 3, 5, 6, 7 and 9, which are divisible by 5 and none of the digits is repeated?
Answer: Option D
Explanation:
Since each desired number is divisible by 5, so we must have 5 at the unit place. So, there is 1 way of doing it.
The tens place can now be filled by any of the remaining 5 digits (2, 3, 6, 7, 9). So, there are 5 ways of filling the tens place.
The hundreds place can now be filled by any of the remaining 4 digits. So, there are 4 ways of filling it.
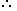 Required number of numbers = (1 x 5 x 4) = 20.
Required number of numbers = (1 x 5 x 4) = 20.
| A. |
| B. |
| ||||||
| C. |
| D. |
|
Answer: Option D
Explanation:
Since each desired number is divisible by 5, so we must have 5 at the unit place. So, there is 1 way of doing it.
The tens place can now be filled by any of the remaining 5 digits (2, 3, 6, 7, 9). So, there are 5 ways of filling the tens place.
The hundreds place can now be filled by any of the remaining 4 digits. So, there are 4 ways of filling it.
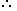 Required number of numbers = (1 x 5 x 4) = 20.
Required number of numbers = (1 x 5 x 4) = 20.Friday, April 15
Thursday, April 14
Chocolate-Banana Milkshake Recipe
Ingredients (2 servings):
2 bananas
2 cups of milk (or soy milk)
2 to 4 tablespoons of ice cream
Method:(10 min)
(1) Peel and cut the banana
(2) Put the banana pieces in the blender container and add half the milk
(3) Blend it well (about 30 sec)
(4) Pour the remaining milk, then add the ice cream
(5) Blend it well (about 30 sec)
(6) Pour the banana milkshake into glass

2 bananas
2 cups of milk (or soy milk)
2 to 4 tablespoons of ice cream
Method:(10 min)
(1) Peel and cut the banana
(2) Put the banana pieces in the blender container and add half the milk
(3) Blend it well (about 30 sec)
(4) Pour the remaining milk, then add the ice cream
(5) Blend it well (about 30 sec)
(6) Pour the banana milkshake into glass

Monday, April 11
Duties of Advocate towards the opponent
- Carry out legitimate promises made.
- Not to negotiate directly with opposing party
- Keep respectful attitude towards the opposition party
- By informing wrong matter, do not misguide opposition
- He should keep friendly relation with opponent
- He should not criticize wrongly and unnecessary of his opponent
- Do not take advante of lack of knowledge of his opponent
Duties of Advocate towards fellow advocates
- Sign board and name plate
- Not promote unauthorized practice of law
- Not advertise or solicit work
- Consent of fellow advocate to appear
- An advocate shall not accept a fees less than the fee, which can be taxed under rules when the client is able to pay more
- He should keep friendly relation with the fellow advocates
- He should not criticize wrongly and unnecessary of his co-advocate
- By taking less fees, he should not compete with his co-advocate
- Do not take advante of lack of knowledge of his co-advocate
Duties of Advocate towards the Court
- Act in a dignified manner
- Respect the court
- Appear in proper dress code
- Not communicate in private to a Judge
- Refuse to act in illegal manner towards the opposition
- Refuse to represent clients who insist on unfair means
- Refuse to appear in front of relations
- Not to wear bands and gowns in public
- Not represent establishments of which he is a member
- Not appear in matters of pecuniary interest
- Not stand as surety for client
- Not to try undue influence on judge
- Should keep respect of judge, should maintain status of judge
- If any near relation with the judge- then advocate should not appear before that judge for process of the case
- Advocate should not waste time of court by taking dates- except in special circumstances
- Advocate should not waste time of court and when the court called out, He should be immediately present
- He should be fully and thouroughly ready with the case to present it
- To give training of law, he should not take money from any person
Duties of Advocate towards his Client
- Duty to charge reasonable fees
- Duty to make full and frank disclosure
- Duty to ensure no conflict of interest
- Duty of care to client
- Duty to maintain confidentiality
- Duty to act only on client's instructions
- Duty to the law
- An advocate shall not, at any time, be a party to fomenting of litigation.
- An advocate shall not act on the instruction of any other person other than his client or authorized agent.
- Not withdraw from service
- Bound to accept briefs
- Not appear in matters where he himself is a witness
- Not suppress material or evidence, which shall prove the innocence of the accused
- Not disclose the communication between client and himself
- Not receive interest in actionable calim
- Keep proper accounts
- Provide copy of accounts
- Intimate the client on amounts
- Not lend money to his client
- Not appear for opposite parties
- Not adjust fees against personal liabily
- Not bid or transfer property arising of legal proceeding
- Should not take signature of client on blank page
- Should not take client's money by fraud
- Should not take property of client on mortage for recovery of fees by advocate
- The work of poor should be done free of charge
Tribunals
Advantages of Tribunals:
- Cheapness
- Accessibility
- Freedom from technicality
- Expert knowledge of their particular subject [i.e. through specialism, which reduces the time needed and thus costs]
- Legally qualified chairmen - helping to ensure justice is done
- The procedure means that if you do not know what you are doing the tribunal will help you.
- Tribunals' local knowledge can be beneficial.
- They allow flexibility since there is little use made of precedent.
- They reduce the workload of government departments.
- They help reduce the workload of the judiciary.
- Reasoned judgments allow for both sides to make amends, for appeals, and for justice to be seen to be done.
- Speedy justice can be piossible.
- There is an unfair imbalance between represented and unrepresented parties - it is unfair to people who are not represented and cannot get legal aid to come up against a rich corporation - since richer parties are allowed to employ skilled representation they are consequently more likely to win.
- The no-costs rule and lack of legal aid penalise poor litigants, although they do keep costs down.
- The lack of fees encourages poor applicants, although it may also result in ill-founded claims.
- They may lack some of the perceived independence of the judiciary.
- It can still be difficult for the people who go to tribunals to represent themselves because of the inherent difficulty in presenting a case in any environment.
- Tribunals can become complex over time - as did the courts - rules of procedure grow up caused by the use of representatives who as a result make representation desirable in future.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)




